There are no items in your cart
Add More
Add More
| Item Details | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Sat Mar 15, 2025
"Education is not the filling of a pail, but the lighting of a fire."
This age-old wisdom perfectly reflects the transformative power of educational opportunities that India education systems, like OBC reservation, aim to ignite among students from historically disadvantaged backgrounds.
In the large competitive landscape of engineering entrance examinations in India, reservation policies serve as crucial balancing mechanisms to ensure educational equity. For countless aspiring engineers from the Other Backward Classes (OBC) community, understanding the nuances of reservation policies can significantly alter their academic trajectory. Yet, many students remain unaware of these benefits or stumble during the application process due to procedural oversights.
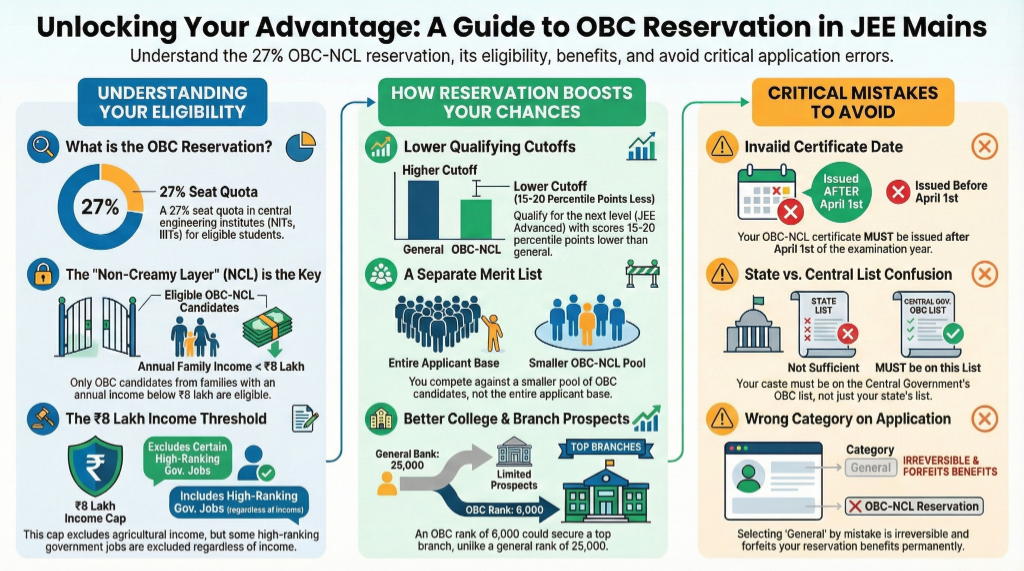
What is OBC Reservation in JEE Mains?
OBC reservation in JEE Mains represents a constitutional provision that allocates 27% of seats in National Institutes of Technology (NITs), Indian Institutes of Information Technology (IIITs), and other Centrally Funded Technical Institutions (CFTIs) for candidates belonging to Other Backward Classes. This provision stems from the government's commitment to educational inclusivity, designed to counterbalance historical social and economic disparities.
The reservation framework operates through the Non-Creamy Layer (NCL) classification, which distinguishes between economically advantaged and disadvantaged sections within the OBC community. Only those falling under the OBC-NCL category can avail themselves of these reservation benefits, creating a targeted approach toward uplifting genuinely disadvantaged sections of society.
JEE Mains Reservation Matrices
Candidates can review the category-wise JEE Main Reservation Criteria for central government institutes in the table below.

For JEE aspirants, the OBC reservation translates into three tangible advantages:
The non-creamy layer classification serves as the cornerstone of the OBC reservation policy, ensuring benefits reach genuinely disadvantaged sections within the OBC community. This economic filter categorises OBC families into:
The OBC-NCL status requires rigorous documentation that must align with specific timelines:
The reservation system substantially lowers entry barriers for OBC-NCL candidates, with qualifying cut offs typically 15-20 percentile points below general category thresholds. This adjustment can profoundly impact students' opportunities:
Improved Branch Allocation
The separate merit list significantly enhances branch allocation prospects for OBC-NCL candidates:
The reservation system typically interconnects with various scholarship and financial assistance programs:
The separate merit list significantly enhances branch allocation prospects for OBC-NCL candidates:
Despite these substantial benefits, many eligible students fail to capitalize on OBC reservation due to procedural errors during application:
Submitting certificates issued before April 1st of the examination year represents the most prevalent mistake. This seemingly minor timing issue leads to automatic category rejection during document verification, forcing candidates into the general pool regardless of their actual OBC-NCL status.
Many students wrongly assume that inclusion in state OBC lists automatically qualifies them for JEE Main reservation. This misconception results in unexpected disqualification during verification rounds when their caste fails to match against the central list.
OBC-NCL certificates must follow the exact format prescribed by NTA. Even minor deviations, missing declarations, or altered phrasings lead to rejection. Local authorities sometimes issue certificates in state-specific formats that prove invalid for JEE purposes.
Category Declaration Oversights
Some eligible students mistakenly select 'General' instead of 'OBC-NCL' during initial registration, erroneously believing they can change their category later by submitting appropriate certificates. This initial declaration proves irreversible after application submission, permanently forfeiting reservation benefits.
Submitting general income certificates instead of specific OBC-NCL declarations represents another common mistake. These documents, though verifying income levels, lack crucial declarations regarding central list inclusion and non-creamy layer status.The consequences of these mistakes prove severe—immediate reclassification as general category candidates, significantly higher cutoff requirements, and vastly reduced admission prospects. For borderline candidates, such errors often translate to outright disqualification from institutions they could otherwise access.
Q1: Can I use my parent's OBC certificate for JEE Main application?
A: No, you must obtain your own OBC-NCL certificate in the prescribed format issued after April 1st of the examination year. Parental certificates are invalid regardless of their validity period.
Q2: My caste appears in my state's OBC list but not in the central list. Am I eligible for reservation?
A: No, JEE Main reservation applies exclusively to castes listed in the central OBC list maintained by NCBC. State list inclusion holds no relevance for central institutions.
Q3: Does agricultural income count toward the ₹8 lakh creamy layer threshold?
A: No, income derived purely from agricultural sources is excluded from the creamy layer determination as per government guidelines.
Q4: I'm an OBC candidate with family income above ₹8 lakh. Can I still claim reservation?
A: No, you would be classified as OBC-Creamy Layer and treated on par with general category candidates without reservation benefits.
Q5: Can I change my category from General to OBC-NCL after submitting my application if I obtain a certificate later?
A: No, category declarations are irreversible after application submission. You must select the correct category and possess valid documentation before applying.
"अपरतिष्ठितः कर्म सर्वत्र विधिष्यते"
Unwavering effort always yields results.
This quote emphasizes the importance of unwavering effort in achieving success. For OBC students preparing for JEE Mains, this means not only working hard academically but also ensuring they utilize the reservation benefits correctly. By combining diligent preparation with a thorough understanding of the OBC reservation system, students can significantly enhance their chances of admission to prestigious institutions like NITs and IIITs. Ultimately, this unwavering effort will yield results, helping them overcome historical disparities and achieve their academic goals. We help Students to achieve there goal. Get the Exclusive Free Mock test for JEE Mains and map your real level of prepartaion. Just Enroll for Free Study Kit for JEE Mains 2025 and get these test free.


Rahul Nandan
Chemistry Expert 🧪| Mentor to Top IIT-JEE, NEET, & Olympiad Achievers 🏆 | Facilitated admissions to MIT, IITs, AIIMS 🎓 | Toastmaster 🎤 | Warren Buffet Enthusiast 💼 | Orator 🗣️ | Music Aficionados🎵